Here are a few examples of recent studies conducted using the ambient table at the SXRMB beamline:
Electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction
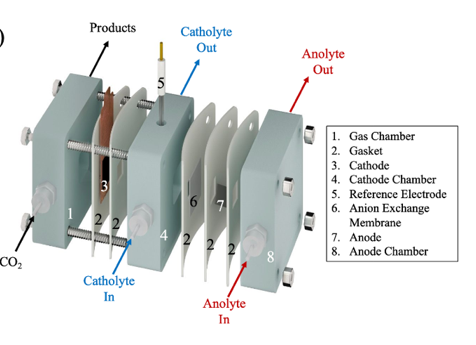
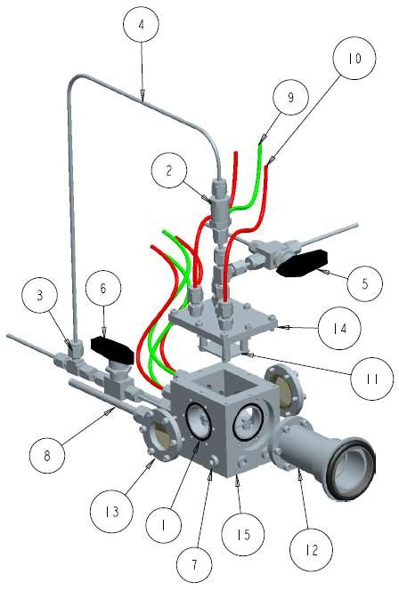
Researchers from McGill University have developed copper nanocluster catalysts for converting carbon dioxide (CO₂) into methane, a cleaner energy source. In-situ measurements were carried out at the ambient table endstation using a modified flow cell, as shown below.
For further information, please refer to the following paper: Selective CO2 to methane conversion
Understanding the role of passivation layers using in-situ solid-state anode-free batteries
The performance of Anode-free sulfide-based all-solid-state lithium metal batteries (ASSLMBs) is largely influenced by the interfacial properties of the current collectors such as copper (Cu) and stainless steel (SS). In this study in-situ synchrotron-based XANES measurement was performed to analyze changes in the local chemical environments of elements in the system and to understand the interphase composition and its impact on electrochemical performance.
Illustration of in-situ cell configuration is shown below:
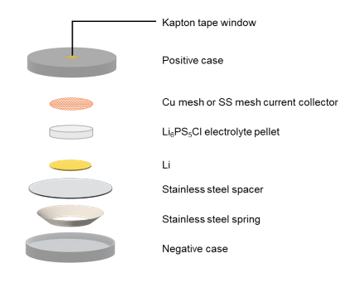
The in-situ cell was placed on the sample holder under a vacuum of 10−7 torr to optimize flux for edges with lower energies. The Cu and SS mesh current collectors were utilized to enable the investigation of interphase evolution during Li plating and stripping. The cell setup of Cu and SS current collectors for in-situ XANES measurements is shown.
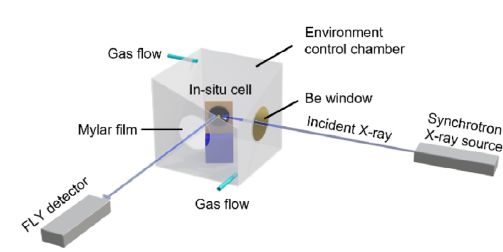
For further information, please refer to the following paper: Revealing the Neglected Role of Passivation Layers of Current Collectors for Solid-State Anode-Free Batteries
In-situ experiment using reaction cell
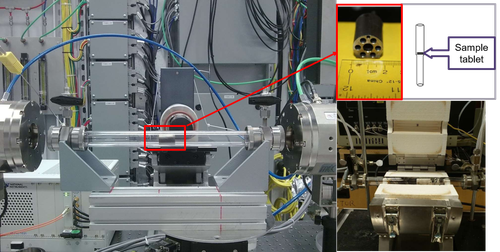
In-situ experiment was performed in a reactor cell as shown below. This reactor is equipped with water-cooled ceramic heaters, with gas inlets for He and/or DMTHF. Powder sample was pressed into pellet, sitting in a sample holder placed onto the heater.
For further information, please refer to the following paper: Investigation of the activity of different NbOx species in Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) reaction
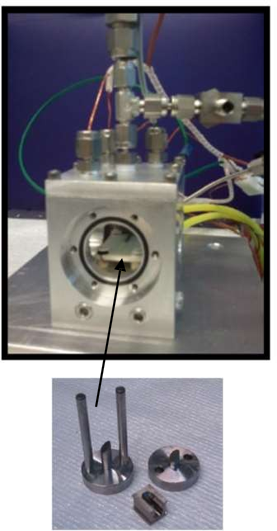
Tube furnace and six shooter sample holder for solid-gas in-situ reactions
For in-situ experiments, 6–8 mg of sample can be loaded into a 6-hole shooter sample holder and placed inside a quartz reactor. The reactor, placed within a tube furnace, is positioned between the first and second ionization chambers to facilitate data collection in transmission mode. In-situ XAS measurements can be conducted in transmission mode using X-ray energies above 5 keV. This setup allows for real-time monitoring of solid-gas reactions under controlled temperature and gas flow conditions, enabling simultaneous XAS data collection.

For more information on these experiments, please refer to a similar study conducted at the 10-BM (bending magnet) beamline at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), Argonne National Laboratory. Metal nanoparticle growth and bimetallic interaction of Ni-based catalysts for CO2 reforming of CH4
Electroreduction of CO₂ using Pd nanoparticles (NPs)
In-situ Pd K edge and L3 edge XAS measurements were performed to identify the systematic engineering of active phases of Pd NPs, which are exploited to select reaction pathways for CO2 electroreduction. The results suggested that the main product, which is either formate or CO, can be selectively produced with high Faradaic efficiencies (>90%) and mass activities in the potential window of 0.05 to −0.9 V with scalable application demonstration.
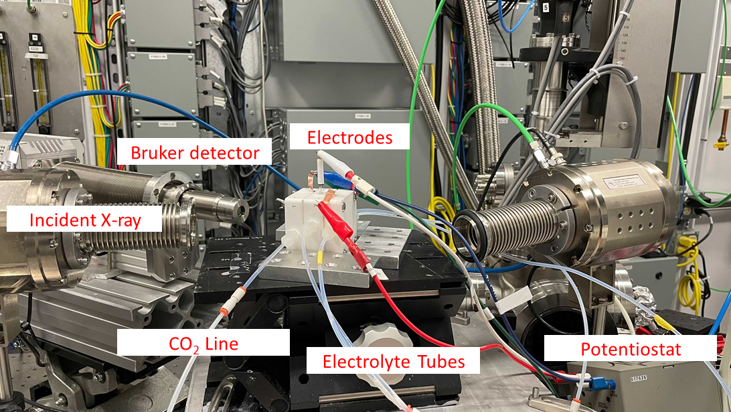
Experimental setup of in situ XAS for CO2 electroreduction is shown below, where (a) is the schematic diagram of in-situ XAS cell and (b) is the photograph of in situ XAS cell in working condition.
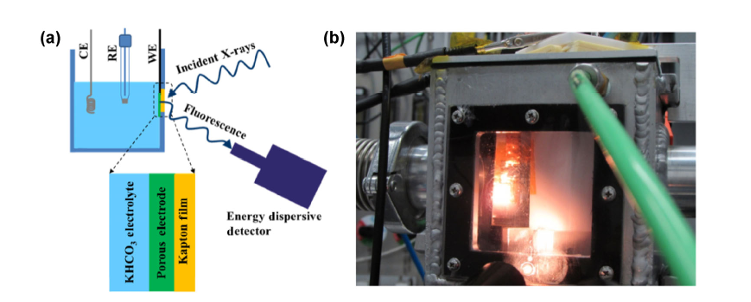
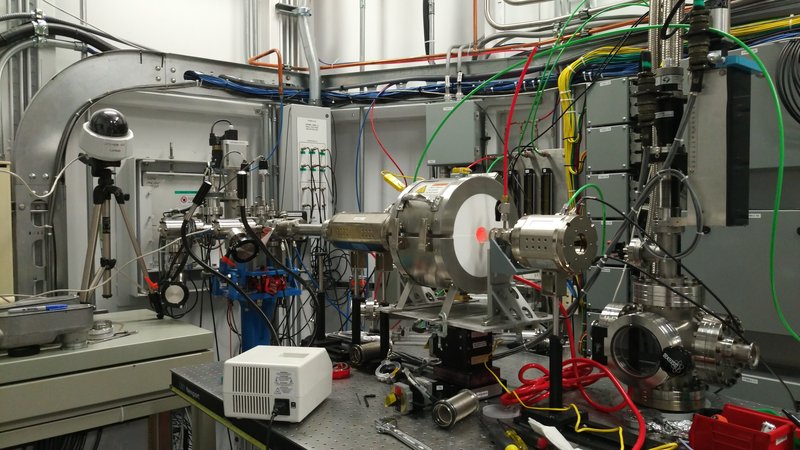
Here is the full setup for the electroreduction of CO₂ using Pd nanoparticles (NPs):
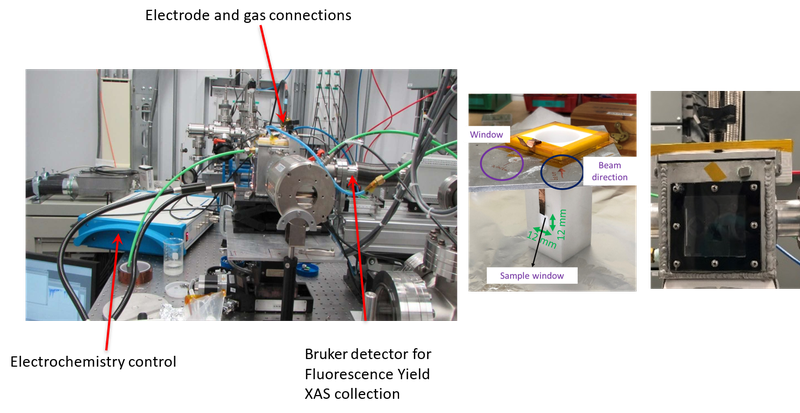
For further information on this research, please refer to the following paper: Switchable CO2 electroreduction via engineering active phases of Pd nanoparticles
Do you have an idea for a new endstation set up? If our beamline does not currently have a set up that will suit your needs, we encourage you to contact us with your ideas!
Sample stage
